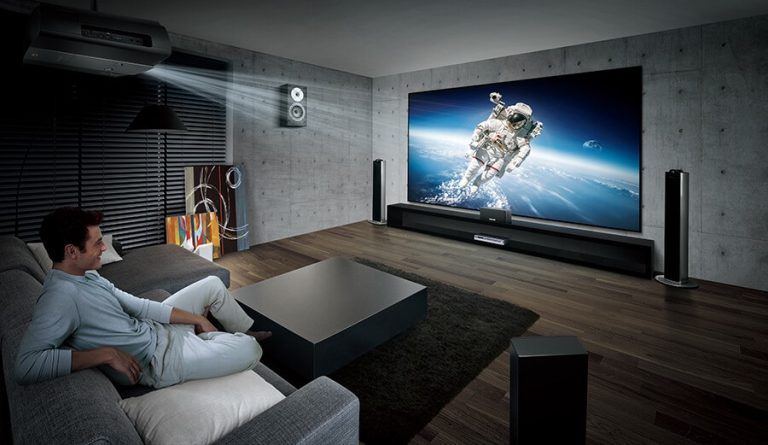
Recently, Ultra Short Throw (UST) projectors have become the most important advancement in projection display technology; offering the ability to project large screens from extremely short distances, UST projectors will dramatically change home entertainment, education, corporate/office collaboration and commercial display settings.
As the demand for large screen displays over 100 inches continues to rise, ultra short throw projectors are quickly becoming a very popular product across the globe. For brands, distributors and solution providers, due to the growing global projector market, it’s important to understand the individual characteristics of UST projectors versus traditional long throw projectors when creating/displaying their next-generation display products.
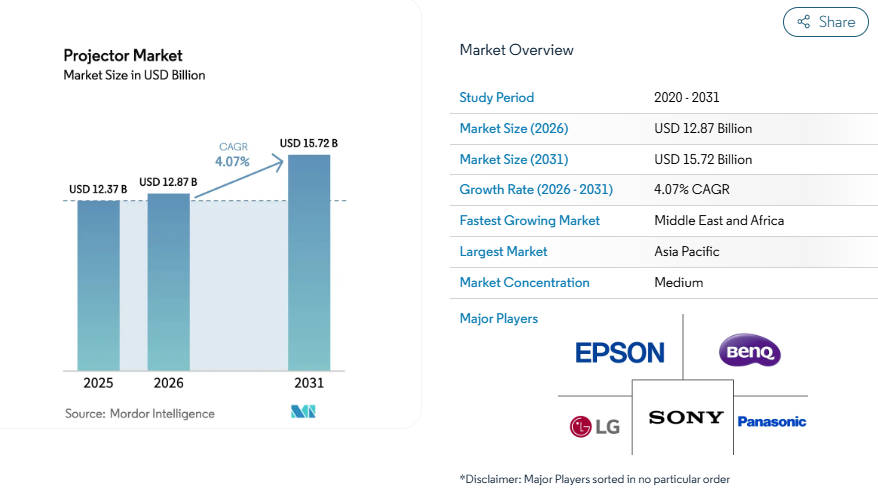
According to market research performed by Mordor Intelligence, projected market growth in the global projector market was estimated at USD 12.37 billion in 2025 and USD 12.87 billion in 2026 with ongoing projected growth through the end of the decade.
Within this market, ultra short throw projectors represent one of the fastest-growing segments due to their ability to deliver immersive large-screen experiences in limited spaces.
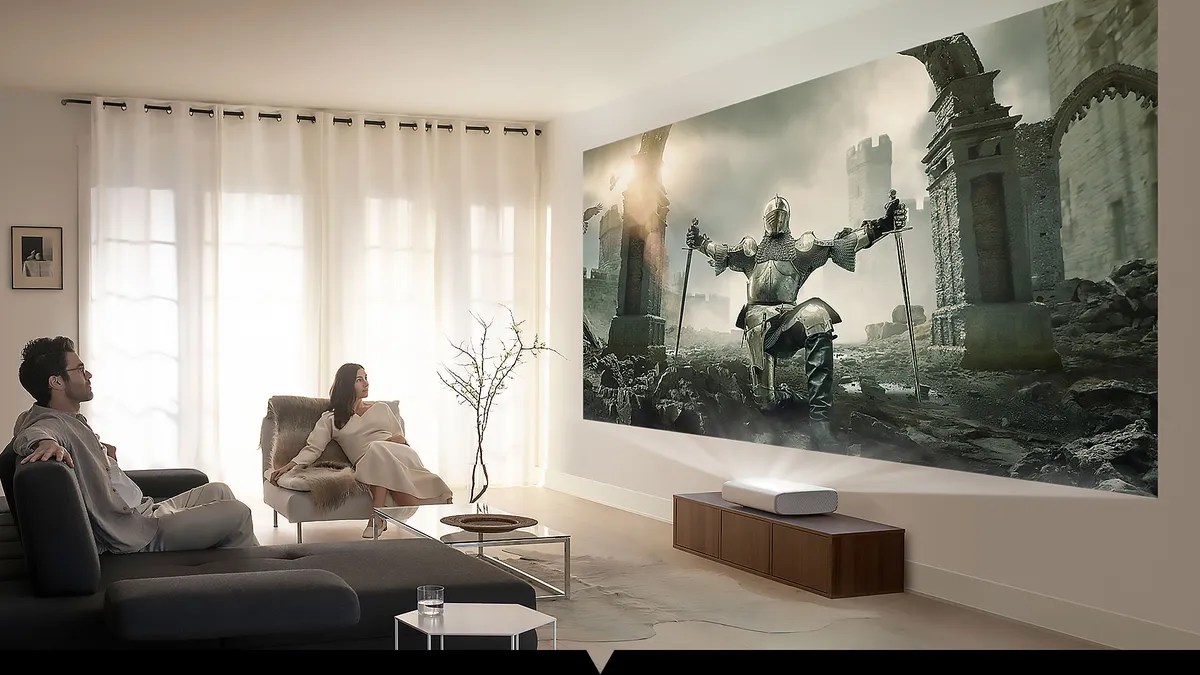

What is an Ultra Short Throw Projector?
An Ultra Short Throw (UST) projector is a projection device designed to create large images from a very short distance between the projector and the screen.
Most UST projectors feature a throw ratio between 0.15:1 and 0.25:1, which allows them to project a 100-inch image from a distance of only 20 to 40 centimeters.
In contrast, traditional long throw projectors typically require a projection distance of 3 to 5 meters to produce the same screen size.
Projection Distance Comparison
Projection distance is one of the most significant differences between UST projectors and traditional projectors.
| Projector Type | Throw Ratio | Distance for 100-inch Screen |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra Short Throw | 0.15:1 – 0.25:1 | 20–40 cm |
| Short Throw | 0.4:1 – 0.8:1 | 1–2 m |
| Long Throw | 1.2:1 – 1.8:1 | 3–5 m |
This extremely short projection distance allows UST projectors to be installed directly in front of the screen, often on a TV cabinet or media console, making them highly suitable for modern living spaces.
Key Advantages of Ultra Short Throw Projectors
Exceptional Space Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of ultra short throw projectors is their ability to deliver large images without requiring deep rooms.
This makes them ideal for environments such as:
Living rooms
Small apartments
Conference rooms
Classrooms
Retail displays
Because the projector sits very close to the screen, installation becomes significantly easier compared with traditional projection systems.
Users can simply place the projector on a cabinet beneath the screen instead of installing ceiling mounts or running long cables across the room.
Elimination of Shadow Interference
Traditional projectors often suffer from shadow interference when someone walks between the projector and the screen.
UST projectors eliminate this problem because the projector is positioned directly below the screen.
Advantages include:
No shadows blocking the image
No bright projection light shining into viewers’ eyes
More comfortable viewing experience
This feature is particularly valuable in education environments, interactive presentations, and meeting rooms where presenters frequently stand near the screen.
Large Screen Display for Living Rooms
Ultra short throw projectors are often referred to as laser TV solutions because they can easily produce extremely large images suitable for living room entertainment.
Typical screen sizes supported by UST projectors include:
100 inches
120 inches
150 inches
New generation models introduced at recent technology exhibitions can even reach 200-inch projection sizes.
For comparison, the average global TV size is approximately 55 inches, according to data from Statista.
This makes UST projectors a compelling alternative to traditional televisions when users want immersive large-screen experiences.
Laser Light Source Technology
Most modern UST projectors use laser light sources, which offer several advantages compared with traditional lamp-based projection systems.
Key benefits include:
Lifespan of 20,000 to 30,000 hours
Stable brightness performance
Instant startup and shutdown
Lower maintenance costs
Some high-end UST projectors also utilize RGB triple laser technology, which provides extremely wide color gamuts.
According to laser display technology reports from Hisense, some triple-laser projection systems can achieve over 100% coverage of the BT.2020 color space, delivering vibrant and accurate color reproduction.
Easier Installation and Deployment
Compared with traditional projectors, UST projectors are significantly easier to install.
Typical UST installation process:
Place projector on a TV cabinet
Position it directly below the projection screen
Connect power and signal sources
Traditional projectors often require:
Ceiling mounting
Long HDMI cables
Careful alignment adjustments
The simplified installation process makes UST projectors especially attractive for home users, offices, and commercial environments.

Limitations of Ultra Short Throw Projectors
Although UST projectors offer many advantages, they also have several limitations that should be considered.
Higher System Cost
The optical system used in ultra short throw projection is more complex than traditional projection systems. As a result, UST projectors generally have higher manufacturing costs.
However, prices have gradually decreased as the technology becomes more widely adopted.
Screen Requirements
Due to the steep projection angle used by UST projectors, image quality is more sensitive to screen surface flatness.
For optimal image performance, many installations recommend using ALR (Ambient Light Rejecting) screens.
ALR screens help improve contrast and brightness in environments with ambient lighting.
Image Geometry Sensitivity
Minor irregularities on the projection surface may cause slight distortion near the edges of the image.
This is a common characteristic of ultra short throw optical systems.
Advantages of Traditional Long Throw Projectors
Traditional long throw projectors still maintain advantages in certain scenarios.
Key advantages include:
Lower product cost
Flexible installation distance
Better image uniformity across the screen
Compatibility with standard projection screens
For dedicated home theater rooms with controlled lighting, long throw projectors can still deliver exceptional cinematic image quality.
Global Market Trends for UST Projectors
The global projector market continues to grow steadily.
According to Grand View Research, the projector market reached USD 3.37 billion in 2022, and growth continues to be driven by large-screen home entertainment demand.
More specifically, the Ultra Short Throw projector market is expanding rapidly.
Market research indicates:
UST projector market size (2025): approximately USD 2.4 billion
Projected market size (2032): over USD 5.3 billion
Estimated CAGR: about 12%
The 4K laser UST projector segment is growing even faster.
Market estimates show:
2024: USD 1.64 billion
2025: USD 1.95 billion
2026: USD 2.3 billion
These numbers demonstrate strong momentum for ultra short throw projection technology.
Regional Market Distribution
The demand for UST projectors varies across regions.
Current global market distribution:
Asia-Pacific — 36.5%
North America — 27.9%
Europe — 20.3%
Asia-Pacific remains the largest market due to strong demand for consumer electronics and rapid adoption of new display technologies.
Applications of Ultra Short Throw Projectors
Ultra short throw projectors are used across multiple industries.
Home Entertainment
UST projectors provide immersive large-screen viewing experiences in living rooms without requiring dedicated home theater rooms.
Education
Teachers can interact with projected content without blocking the image, making UST projectors ideal for modern classrooms.
Corporate Meeting Rooms
UST projection systems are widely used for presentations, video conferences, and collaborative workspaces.
Retail and Commercial Displays
Retail stores and exhibition spaces use UST projection to create immersive visual displays that attract customer attention.

Conclusion
Ultra Short Throw projectors represent one of the most important advancements in projection display technology.
Compared with traditional long throw projectors, UST systems offer:
Extremely short projection distances
Superior space efficiency
Elimination of shadow interference
Simplified installation
Large screen viewing experiences suitable for living rooms
As global demand for large-screen entertainment and smart display solutions continues to grow, ultra short throw projectors are expected to become an increasingly important segment of the projection industry.
UST projectors can project large images from less than half a meter away, while traditional projectors require several meters of projection distance.
Yes. UST projectors are designed for living room environments because they require minimal space and eliminate shadow interference.
While they can project onto a wall, using an ALR screen is recommended to improve brightness and contrast.
Most ultra short throw projectors support screen sizes between 80 inches and 150 inches, with some new models reaching 200 inches.